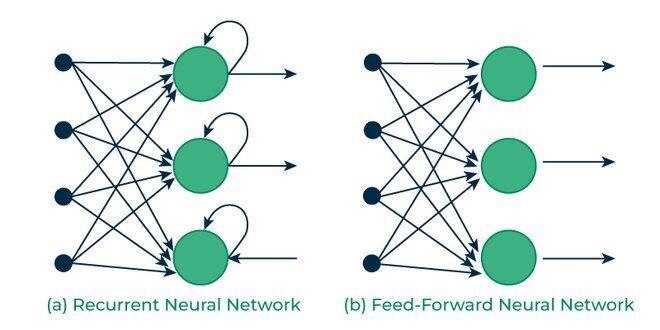
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are a type of artificial neural network designed to work with sequential or time series data[1][2]. Unlike traditional feedforward neural networks, RNNs have a unique ability to retain information from previous inputs, effectively giving them a form of memory[3].
The key feature of RNNs is their feedback loop, which allows information to be passed within a layer[2]. This loop enables the network to maintain a hidden state, capturing sequential dependencies by remembering previous inputs while processing current ones[1]. This makes RNNs particularly well-suited for tasks involving sequential data, such as:
- Language modeling and text generation
- Speech recognition
- Machine translation
- Image captioning
- Time series forecasting[1][5]
How RNNs Work
RNNs process data sequentially, with each step taking two inputs:
- The current input data point
- The hidden state from the previous step
The network then produces an output and updates its hidden state[3]. This process can be “unfolded” in time, creating a structure that resembles a very deep feedforward network, with each layer representing a time step[3].
Training RNNs
RNNs are trained using a technique called Backpropagation Through Time (BPTT)[3][5]. This is an extension of the standard backpropagation algorithm, adapted to work with the unfolded structure of RNNs. However, training RNNs can be challenging due to issues like vanishing and exploding gradients, especially when dealing with long sequences[1][5].
Variants of RNNs
To address the limitations of basic RNNs, several variants have been developed:
-
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): LSTMs introduce a more complex unit with gates that control information flow, allowing the network to better capture long-term dependencies[1][5].
-
Gated Recurrent Units (GRU): Similar to LSTMs but with a simpler structure, GRUs use reset and update gates to control information flow[5].
-
Bidirectional RNNs: These process sequences in both forward and backward directions, allowing the network to capture context from both past and future states[1].
RNNs and their variants have become fundamental components in many state-of-the-art solutions for sequential data processing tasks, playing a crucial role in advancing fields like natural language processing and speech recognition[4][5].
Further Reading
1. Introduction to Recurrent Neural Network – GeeksforGeeks
2. A Brief Introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks | by Jonte Dancker | Towards Data Science
3. An Introduction to Recurrent Neural Networks and the Math That Powers Them – MachineLearningMastery.com
4. [1912.05911] Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): A gentle Introduction and Overview
5. What Is a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)? | IBM
Description:
Sequential data processing, time-series forecasting, and anomaly detection.
IoT Scenes:
Predictive maintenance, environmental monitoring, and time-series forecasting.
Predictive Maintenance: Forecasting equipment failures based on time-series data.
Environmental Monitoring: Analyzing sensor data over time for anomaly detection.
Energy Management: Predicting energy consumption patterns and optimizing usage.
Speech Recognition: Converting spoken commands into actionable data in smart assistants.