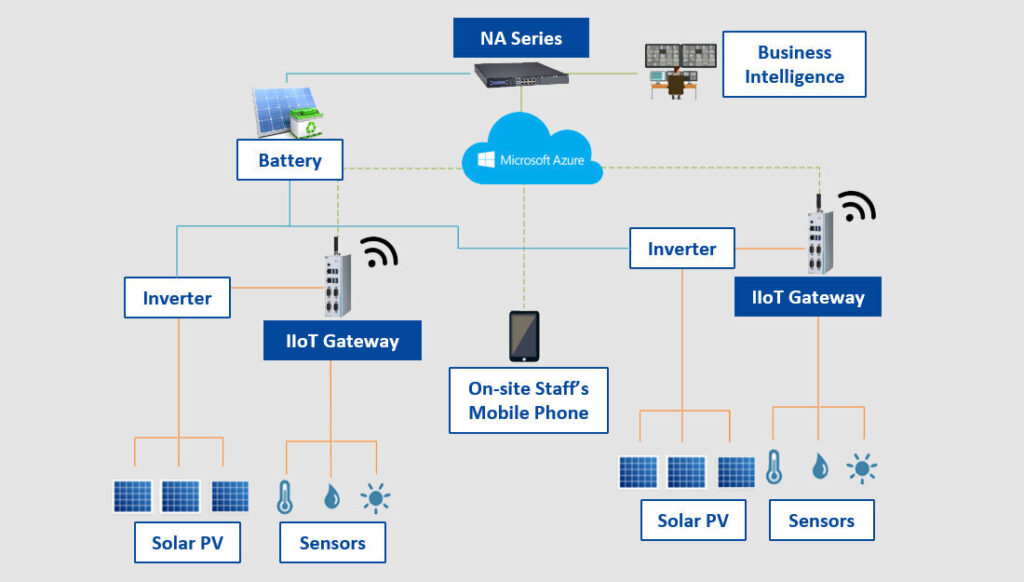
Smart Grid Management integrates advanced technologies to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of electricity distribution systems. Key components of smart grid management include Predictive Analytics, Anomaly Detection, and Sensor Fusion, which utilize artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize grid operations.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics plays a crucial role in smart grid management by analyzing data from various sources, such as smart meters and sensors, to forecast potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach allows utility companies to implement predictive maintenance strategies, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. For instance, Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) employs machine learning algorithms to predict equipment failures, enabling timely interventions that prevent outages[2].
Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection is essential for identifying irregular patterns in grid operations that may indicate underlying problems. By continuously monitoring data streams from grid components, AI models can detect deviations from normal behavior, triggering alerts for further investigation. This capability enhances system reliability and safety, as potential faults can be addressed before they lead to significant failures. E.ON, a German energy company, has successfully implemented AI-driven anomaly detection to minimize faults in their electricity grid[2].
Sensor Fusion
Sensor fusion involves integrating data from multiple sensors to create a comprehensive view of grid performance. This technique enhances decision-making by providing a more accurate representation of the grid’s status. By combining data from various sources, such as weather conditions, energy consumption patterns, and equipment health, utilities can optimize energy distribution and improve demand response strategies. The integration of sensor data is vital for managing the complexities of modern energy systems, especially with the increasing penetration of renewable energy sources[4][3].
Conclusion
The implementation of AI models such as Predictive Analytics, Anomaly Detection, and Sensor Fusion is transforming smart grid management. These technologies not only improve operational efficiency and reliability but also contribute to the sustainability of energy systems. As utilities continue to leverage these advanced analytics, the future of smart grids looks promising, with enhanced capabilities for managing the challenges of energy distribution in a rapidly evolving landscape[1][5].
Further Reading
1. The Role of Data Analytics in a Smart Grid | GE Vernova
2. Predictive Maintenance in Smart Grids | CLOU GLOBAL
3. Big data analytics in smart grids: a review | Energy Informatics | Full Text
4. A-Z of Smart Grid Analytics
5. Predictive Analytics: The Future of Smart Grid Reliability